Electrical Engineering and Railways
DC Series Motor as Traction Motor
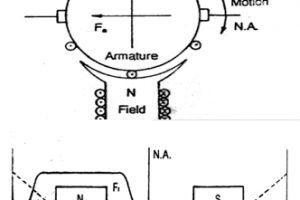
Last updated on April 5th, 2015 at 06:14 am There are two basic principles which governs the working of DC machine A current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force demonstrated by Lorentz Law. Direction of the force is given by Fleming’s LH rule. A voltage is induced in the conductor […]
Braking Effort
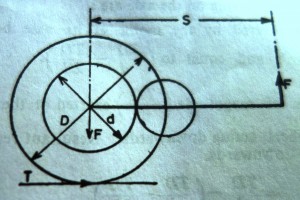
Last updated on April 5th, 2015 at 06:14 am Braking effort is the effort required to stop the train within safe braking distance. It has safety consequences. Braking effort is required to counter the kinetic energy of train running at a speed V and can be expressed as . where D is braking […]
Weight Transfer
Last updated on April 5th, 2015 at 06:14 am When a locomotive is standing still on straight track, its weight is uniformly distributed on all axles but during traction, reactive forces and turning moments re-distributes the loading on each axle. System for transmission of Tractive effort from wheel to axle-bogie-body-draw bar pull results into non-uniform […]
Wheel Slipping and Sliding
Last updated on March 23rd, 2014 at 05:02 pm Wheel slipping occurs when tractive effort exceeds adhesive weight whereas sliding occurs when braking effort exceeds adhesive weight. In both the situations, it is the adhesive weight playing the most important role. Adhesive weight is defined as the force that can be exerted by a […]
Tractive Effort
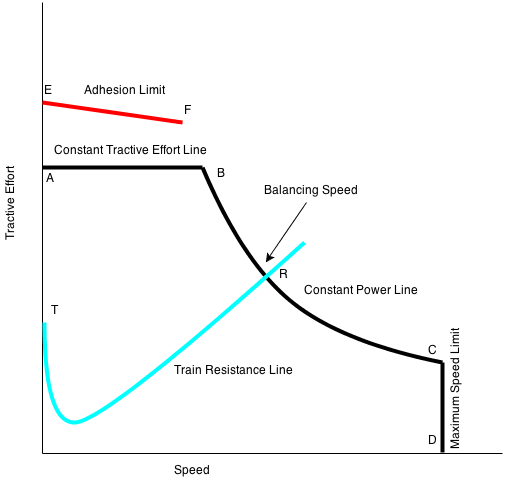
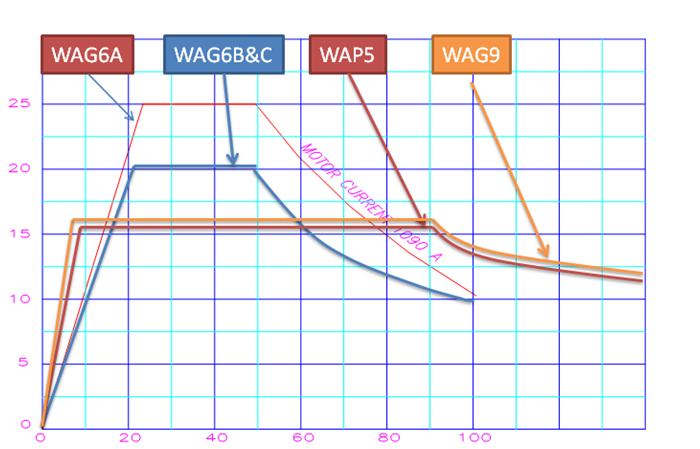
Last updated on July 29th, 2019 at 04:51 am Tractive effort is the force required to haul a load. Tractive effort, when multiplied with speed at which the train is required to run, gives the HorsePower. Importance of Tractive effort lies with its capability to start a train on the gradient and run it up […]
Train, grade, curve and Acceleration Resistance
Last updated on February 6th, 2017 at 10:19 am Trains resistance is defined in terms of force required to encounter resistance arising due to vehicle, track, grade, curve, acceleration, wind at different time and place etc. Study of these resistances and its impact in train motion is important to develop strategies for reducing it. It […]
Adhesion
Last updated on April 5th, 2015 at 06:13 am Adhesion is one of the most important term used in Railways parlance signifying the ability of efficient heavy haul and safe braking. Adhesion limits the tractive and braking effort per traction and braking wheel respectively. On Indian Railways, adhesion limitation has caused more concern of wheel […]
Energy Conservation – Renewable sources of Energy

Last updated on May 23rd, 2017 at 10:58 am Most of the modules for tapping using solar power available in the market are from the demand of Industry, residential and office complex. These modules may not immediately suit the Railways requirement. It is therefore necessary to identify the economic usage of the solar energy specific […]
Energy Conservation – Train Lighting and Air Conditioning

Last updated on March 2nd, 2018 at 03:20 am Power supply for Train Lighting and air conditioning is provided either by Self generation or End on Generation system. Estimation of energy consumption for Train Lighting and Air Conditioning SG Coaches Holding of Self Generation Coaches: AC=8000; Non-AC=38000 Installed Capacity of power Generation = No. of […]
Energy Conservation -Traction

Last updated on April 5th, 2015 at 06:13 am Traction Energy- Scenario Indian Railways consumed 14.2 B-unit electrical energy and 2.6 B-liters of diesel oil for electrical and diesel Traction respectively during 2011-12. Responsibility for energy conservation in electrical energy lies with the electric department whereas for diesel oil with the Mechanical Department of […]