Types of Maintenance
Maintenance is generally prescribed as Preventive, Directed and Breakdown Maintenance.
Preventive Maintenance consists of Schedule Inspection and Overhauls. Breakdown Maintenance is not actually maintenance but repair when the equipment had a defect arising not anticipated at design or maintenance stage. Directed maintenance is based on the monitoring of the condition of the equipment either physical or defect detection through instrumentation.
Preventive Maintenance started with a simple concept of cleaning, lubrication and replacement of worn out parts. But with time, when we learn about the in-service performance of the equipment, check list, premature replacement of parts get introduced. The items on this list keep on adding with new learnings every day based on failure investigation. Sometimes preventive maintenance becomes a long list of checks…Why it is so? Have you ever thought of the reason?
Let us study and design it in a different manner.
The demarcation between the scope of these three maintenance and individual role in maintenance performance is important for designing maintenance standards. For better understanding, let maintenance be defined as ‘Natural’ and ‘Unnatural’.
Natural Maintenance
This maintenance is a need towards the active and passive services performed by equipment or a body. It consists of
- Cleaning, lubrication, replacement of worn out parts performing intense duty or due to wear and tear,
- Replacement of parts which has lived its natural life such as rubber items, white washing, painting etc.
- To monitor the condition of the equipment through instrumentation which are not easily accessible avoiding its dismantling
This maintenance need is a design feature and perceived at the design stage itself. Maintenance content does not change unless design changes are undertaken, therefore called natural, fixed or static maintenance.
Unnatural Maintenance
- Even if the natural maintenance activity is performed to a good standard, the equipment may still fail due to design, manufacturing, maintenance deficiency, defective material, abuse, wrong handling and theft.
- This has not been anticipated at the design or manufacturing stage. This is also a class of maintenance which take away a large amount of time, money, manpower etc.
This maintenance need for this aspect is not envisaged at design stage. It is developed depending upon the learning and experiences during the service of the equipment. Maintenance is unnatural in nature or also called Variable or Dynamic maintenance.
There are two parts of Unnatural Maintenance namely
- A Cause identified and short or long term solution found and under implementation
- B Breakdown occurring due sudden defect arising not anticipated at any stage or natural and Unnatural Maintenance (A) not done properly
Preventive Maintenance
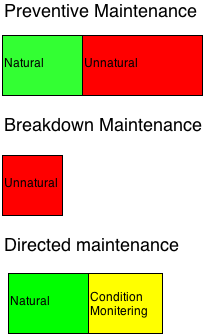
Preventive Maintenance is now defined as a sum of Natural and part of Unnatural maintenance (A) for which solution not yet known and accepted as avoidable through regular check, premature overhauling or replacement of parts etc.
Breakdown Maintenance
Breakdown Maintenance also called as unscheduled or Repairs is defined as attention to equipment for its inability to perform and not finding place in the unnatural part (B) of preventive maintenance. This is towards the balance part of the unnatural maintenance.
Directed Maintenance
Directed or Predictive Maintenance is defined as sum of natural and part of unnatural maintenance derived based on condition monitoring to achieve a high level of reliability.
Directed maintenance has the distinct advantage over preventive maintenance which permits the equipment to live its full life before required to open up. With the development of advanced instrumentation, it is possible to probe and identify the condition of the equipment within minimum possible time and open up only when parameters show a decline. The purpose is to create an environment in which equipment speaks out its problem in a machine language which the testing instrument or maintenance man can understand.
- Directed maintenance shall help in deciding the intervals between two overhauling schedules.
- It reduces maintenance cost
- It improves reliability by identifying defects vulnerable to breakdown
This can well be represented by the block diagram as follows:
The width of the maintenance block above depends upon inbuilt reliability, cost of maintenance activity wise and it’s implication towards inconvenience. Look at the household items all around and their maintenance need. What you notice? Most of the items are maintenance free and balance required maintenance to the extent of cleaning and in some cases change of lubrication. This situation is taking shape even for road vehicle also. Development of maintenance free technologies to benefit user is the most important marketing strategy.
Dynamism of Maintenance
Split the maintenance need vertically into two separate heading, one for natural or Static or Fixed maintenance and another for Unnatural or Dynamic or Variable maintenance.
- The dynamic maintenance capsule shall keep on reducing with implementation of modifications, action plan etc. So that total maintenance input reduces, availability and reliability improves, the cost of maintenance reduces.
- Dynamic maintenance will show a sign of going up as soon as something ‘wrong’ (bad material, workmanship, design, manufacturing) enters the system which is very likely to happen. The dynamic Maintenance head will alert the management to identify the wrong which led to increase in this maintenance.
- Dynamic head will keep define the maintenance challenge clearly and will alert the designer and manufacture as well as.